Potatoes are a versatile and widely consumed root vegetable that comes in various types, each with unique characteristics and uses in commercial foodservice. From russet potatoes with their high starch content ideal for baking and frying to waxy varieties like red bliss potatoes that hold their shape well in dishes like potato salad, there is a potato type suited for every culinary need. Understanding the differences between types of potatoes is essential for chefs and foodservice operators to create delicious and visually appealing dishes.
Shop Bulk PotatoesPotato Textures and Uses
Potatoes are categorized by the texture of their flesh which can indicate the best way to prepare them. These are the three classifications of potato texture:
- Starchy Potatoes: Starchy potatoes have a high starch content with dry, mealy flesh. The dry flesh soaks up liquids like a sponge while the interior causes it to crumble and break down easily, which makes it ideal for making mashed potatoes or using as a baked potato. Potatoes with a high starch content are also the best candidates for frying into french fries.
- Waxy Potatoes: Waxy potatoes contain very little starch and have creamy flesh with a high moisture content. These potatoes usually have thin skin that doesn't need to be peeled before cooking. Because waxy potatoes hold their shape while cooking, they are ideal for simmering in soups and stews, boiling for potato salads, or baking in casseroles.
- All-Purpose Potatoes: All-purpose potatoes contain a medium amount of starch, which gives them a fluffy texture when mashed or baked. But they also have a medium water content, which helps them to hold their shape when simmered, roasted, or pan-fried. Choosing an all-purpose potato provides the most options when it comes to different cooking methods and preparation styles.
Different Types of Potatoes
There are thousands of types of fresh potatoes grown worldwide, but only a fraction of that number are grown commercially in the US. Each variety has been cultivated over time to enhance characteristics like size, texture, and skin type. To help you choose the right potato for your menu, we've made a list of the most popular potato varieties and their uses.
1. Russet Potato

Russet potatoes, also known as Idaho potatoes, are highly recognizable for their ruddy, dark brown skin, oblong shape, and large size. Because they are starchy, Russet potatoes absorb flavors well, ideal for loaded baked potatoes. The thick skin of a Russet crisps up while baking and the interior becomes light and fluffy, perfect for holding toppings like butter, cheese, or sour cream. Russets are also great for mashing, as long as the skins are peeled first. Idaho potatoes are ideal for cutting into french fries because the large size produces a high yield and the potato texture crisps up when deep fried while remaining soft and fluffy on the inside.
- Russet Potato Texture: Starchy
- Russet Potato Skin Color: Medium to dark brown skin
- Russet Potato Flesh Color: Pale white flesh
- Best Uses for Russet Potatoes: Baking, mashing, or deep frying
- Other Names for Russet Potatoes: Idaho Russet, Idaho potatoes
Idaho vs Russet Potatoes
Idaho and Russet potatoes are often used interchangeably in the culinary world. The term "Idaho" when referring to potatoes simply indicates the location of the harvest, with Idaho being a prominent Russet potato-growing region known for its high-quality produce.
2. New Potatoes

New potatoes aren't actually a potato variety. These small potatoes are the young, early harvested potatoes of several varieties. They're collected shortly after the potato plant has flowered, typically between late spring and early summer. These potatoes are characterized by their thin, delicate skins with creamy flesh. New potatoes fall under the waxy category and can be roasted whole without removing the skins, making them well-suited for salads, roasting, and boiling. Their high moisture content also contributes to their slightly sweet flavor. Best eaten within a few days of the harvest, baby potatoes are not good candidates for long-term produce storage.
- New Potatoes Texture: Waxy
- New Potatoes Skin Color: Assorted skin colors
- New Potatoes Flesh Color: Assorted flesh colors
- Best Uses for New Potatoes: Boiling, roasting, or steaming
- Other Names for New Potatoes: Baby potatoes, Petite potatoes
3. Yukon Gold Potato

The Yukon Gold potato is one of the most popular potato varieties because it falls into the all-purpose category. Yukon Golds have thin gold skin that doesn't need to be peeled before cooking. Their striking golden flesh adds a pop of color to your recipes. Yukon Gold potatoes have a buttery and slightly sweet flavor, making them ideal for roasting, baking, mashing, and frying. Their medium-starch content gives them a creamy texture when cooked, perfect for dishes like mashed potatoes or potato salads. These potatoes hold their shape well when cooked, making them suitable for gratins, casseroles, and soups. Use just about any cooking method for these gold potatoes and you won't be disappointed with the results.
- Yukon Gold Potato Texture: All-purpose
- Yukon Gold Potato Skin Color: Golden tan skin
- Yukon Gold Potato Flesh Color: Yellow flesh
- Best Uses for Yukon Gold Potatoes: Boiling, baking, mashing, frying, roasting
- Other Names for Yukon Gold Potatoes: Yukons, Golden Potatoes
Russet vs Yukon Gold
Russet and Yukon Gold potatoes are two of the most popular varieties used in commercial foodservice operations. Russet potatoes are excellent for creating dishes that require a fluffy or crispy texture, while Yukon Gold potatoes are better suited for recipes with a rich consistency. Russet potatoes need to be peeled before making dishes like mashed potatoes, but are excellent for french fries. Yukon potatoes do not need to be peeled prior to cooking and hold their shape well after cooking, making them perfect for dishes like potato salads, gratins, and roasted potatoes.
4. Kennebec Potato
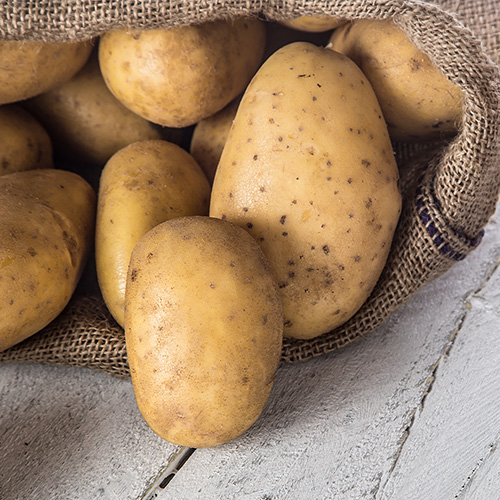

Kennebec potatoes are known for their smooth, thin, light-brown skin and white flesh. They are prized for their neutral and slightly nutty flavor profile, which allows them to easily absorb seasonings and flavors. One of the key features of Kennebec potatoes is their high starch content, which gives them a fluffy texture when cooked. This makes them perfect for making mashed potatoes, french fries, and other dishes that require a soft consistency. Many chefs consider the Kennebec potato to be the best frying potato, so much so that it's common to see the Kennebec name called out on their menu. Instead of french fries, you might see Kennebec fries listed with a menu description that highlights the qualities of the potato. Kennebecs have a unique, nutty flavor and the perfect balance of starchiness and moisture that results in a crispy, golden fry.
- Kennebec Potato Texture: All-purpose
- Kennebec Potato Skin Color: Light tan or beige skin
- Kennebec Potato Flesh Color: Pale white flesh
- Best Uses for Kennebec Potatoes: Deep frying, chipping
Kennebec Potatoes vs Yukon Gold
Yukon Gold and Kennebec potatoes are both all-purpose potatoes. Kennebec potatoes are known for their golden skin and high starch content, making them ideal for frying and baking due to their ability to hold their shape. On the other hand, Yukon Gold potatoes have a buttery texture and thin light-brown skin, making them well-suited for mashing and roasting.
5. All Blue Potato

Blue potatoes like the All Blue variety have dark purple skin and purple flesh that comes from a high concentration of the antioxidant, anthocyanin. This healthy flavonoid is also present in other dark purple produce, like blueberries, red onion, or eggplant. All Blue potatoes are classified as all-purpose, which makes them useful for a variety of cooking methods. They have a higher starch content than other blue potatoes, so reach for this potato to make a vibrant and naturally colored blue mash. All Blues can be easily identified from other blue varieties by a pale ring in their purple flesh.
- All Blue Potato Texture: All-purpose
- All Blue Skin Potato Color: Dark purple skin
- All Blue Flesh Potato Color: Lavender to purple flesh with a pale ring around the edge
- Best Uses for All Blue Potatoes: Boiling, baking, mashing, frying, roasting
6. Adirondack Blue Potato

The Adirondack Blue potato is a purple variety that features brightly colored skin and flesh that keeps its violet hue after cooking. These potatoes are named after the Adirondack Mountains in upstate New York, where they were first developed. Other purple potato varieties lose some of their pigment and turn a grayish color when cooked, which makes the Adirondack Blue a great choice when you want to showcase the vibrant color. These potatoes are often combined with red and white varieties to make a red, white, and blue potato salad for 4th of July menus. Even though they are classified as all-purpose, Adirondack Blue potatoes tend to be waxy and hold their shape when boiled or roasted.
- Adirondack Blue Potato Texture: All-purpose
- Adirondack Blue Potato Skin Color: Dark purple skin
- Adirondack Blue Potato Flesh Color: Dark purple flesh
- Best Uses for Adirondack Blue Potatoes: Boiling, roasting, or steaming
All Blue Potato vs Adirondack Blue Potato
All Blue potatoes and Adirondack Blue potatoes are two popular varieties known for their vibrant blue-purple flesh and skin. All Blue potatoes have a higher starch content, making them ideal for baking, mashing, and frying. On the other hand, Adirondack Blue potatoes have a waxier consistency and a slightly sweeter flavor, making them great for salads, roasting, and boiling. All Blue potatoes will have a pale ring around the edge of their flesh to help identify them.
7. Red Bliss Potato
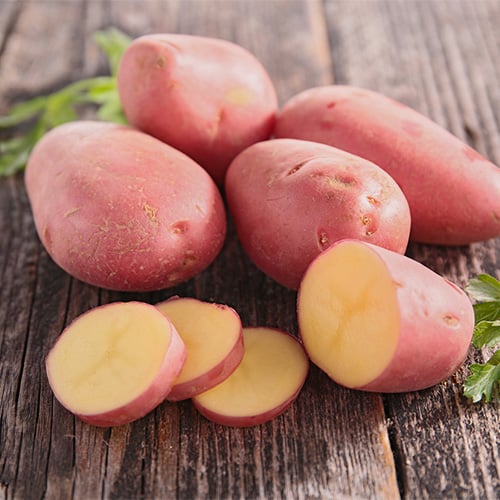

Red Bliss potatoes are a popular variety known for their smooth, thin red skin and firm flesh, adding visual appeal to dishes when left unpeeled. This makes them an excellent choice for recipes where presentation is important, such as roasted vegetable medleys or potato salads. The Red Bliss potato is a waxy potato, which means it has a high moisture content and keeps its shape while cooking. Normally, this type of potato isn't the best choice for mashing, but Red Bliss potatoes have a tradition of being used as a mashing potato despite their texture. You won't achieve a smooth mash with Red Bliss, but the thin red skins require no peeling, and the sweet, buttery flesh is complemented by garlic, herbs, and lemon.
- Red Bliss Potato Texture: Waxy
- Red Bliss Potato Skin Color: Red skin
- Red Bliss Potato Flesh Color: Pale white flesh
- Best Uses for Red Bliss Potatoes: Boiling, baking, mashing, roasting
Red vs Gold Potatoes
Red and gold potatoes are two popular varieties that offer distinct flavors and textures for commercial kitchens. Red potatoes have thin, smooth skins and a waxy texture, making them ideal for boiling, roasting, or using in salads. Their firm, creamy flesh holds up well in soups and stews. On the other hand, gold potatoes have a buttery flavor and a fluffy texture, perfect for mashing or baking. Their thin skins can be left on for added nutrients and color in dishes like casseroles or gratins.
8. German Butterball Potato
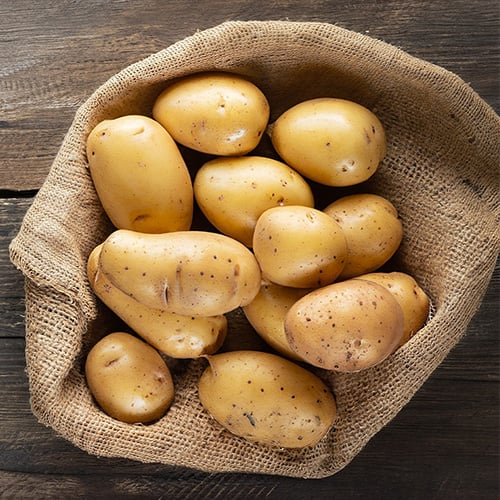

German Butterballs are medium-to-large sized potatoes, characterized by their smooth, golden skin and vibrant yellow flesh. This potato has slightly flakey skin that features a fine webbing along it. German Butterballs are a popular choice among chefs and foodservice professionals due to their versatile nature and rich, buttery flavor. Know for their rich flavor profile, German Butterball potatoes are ideal for a wide range of culinary applications. Their medium starch content makes them suitable for boiling, baking, and mashing, while their waxy texture allows them to hold their shape well when cooked.
- German Butterball Potato Texture: All-purpose
- German Butterball Skin Potato Color: Golden tan or beige skin
- German Butterball Flesh Potato Color: Yellow flesh
- Best Uses for German Butterball Potatoes: Boiling, baking, mashing, frying, roasting
German Butterball Potato vs Yukon Gold
German Butterball potatoes and Yukon Gold potatoes are both yellow potatoes with golden skin. You can differentiate a German Butterball from other yellow varieties like Yukon Gold by the texture of its skin. German Butterballs have thin skin with a flaky texture and the appearance of fine webbing that covers the whole potato. Yukon Gold potatoes have a slightly sweeter flavor than German Butterballs.
9. Red Thumb Potato

The Red Thumb potato is a fingerling potato with red skin and creamy pink flesh. These small to medium-sized potatoes are often sought after for their unique appearance and slightly nutty taste. Fingerlings, just as the name implies, have a finger-like shape that's long and tubular. Their unique shape and small size make them ideal for roasting whole and serving alongside an entree or salad. Because of its attractive, pink and marbled flesh, the Red Thumb is a popular choice in gourmet settings. Red Thumb fingerlings are not a good choice for mashing or deep frying because of their size and shape.
- Red Thumb Potato Texture: Waxy
- Red Thumb Potato Skin Color: Rosy red skin
- Red Thumb Potato Flesh Color: Marbled pink and white flesh
- Best Uses for Red Thumb Potatoes: Roasting, grilling, boiling, pan frying
Red Bliss Potatoes vs Red Thumb Potatoes
Red Bliss potatoes and Red Thumb potatoes are popular varieties known for their vibrant red skin and creamy texture. Red Bliss potatoes are small to medium-sized with smooth, thin red skin and firm, waxy flesh that holds its shape well when cooked. They are ideal for roasting, boiling, and salads. On the other hand, Red Thumb potatoes are smaller in size, elongated, and have a slightly nutty flavor.
10. Russian Banana Potato
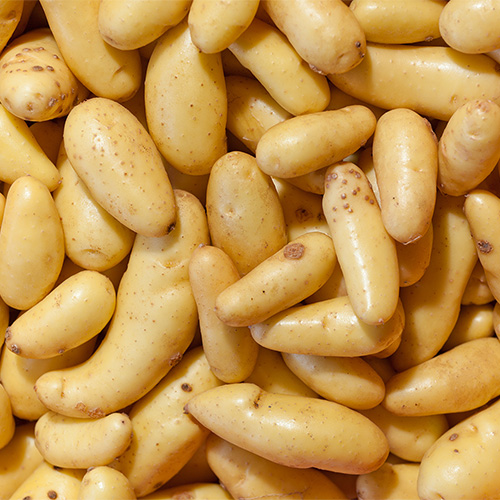

The Russian Banana potato is a fingerling potato that gets its name from its yellow flesh and curved, crescent-like shape. These potatoes typically range from 2 to 4 inches in length and have thin, smooth yellow skin. Like other fingerlings, this waxy potato doesn't need to be peeled and can be roasted whole or boiled for potato salads or roasted vegetable medleys. It's a popular culinary choice due to its sweet, buttery flavor and unique shape. Russian Banana fingerlings are not the best candidates for making mashed potatoes or deep frying due to their small size.
- Russian Banana Potato Texture: Waxy
- Russian Banana Skin Potato Color: Golden tan or beige skin
- Russian Banana Flesh Potato Color: Yellow flesh
- Best Uses for Russian Banana Potatoes: Roasting, grilling, boiling, pan frying
11. Purple Peruvian Potato

Originating from South America, Purple Peruvian potatoes are known for their vibrant purple skin and flesh, making them a favorite among chefs looking to create visually appealing dishes. This potato has the small, slender shape of a fingerling but differs in texture from other varieties in this classification. While most other fingerlings are waxy, this violet tuber has dry, starchy flesh that's sometimes compared to a Russet potato. Because of this, Purple Peruvians can be used for mashing or deep frying.
- Purple Peruvian Potato Texture: Starchy
- Purple Peruvian Potato Skin Color: Dark purple skin
- Purple Peruvian Potato Flesh Color: Solid or marbled purple flesh
- Best Uses for Purple Peruvian Potatoes: Mashing, baking, roasting, chipping
12. Japanese Sweet Potato
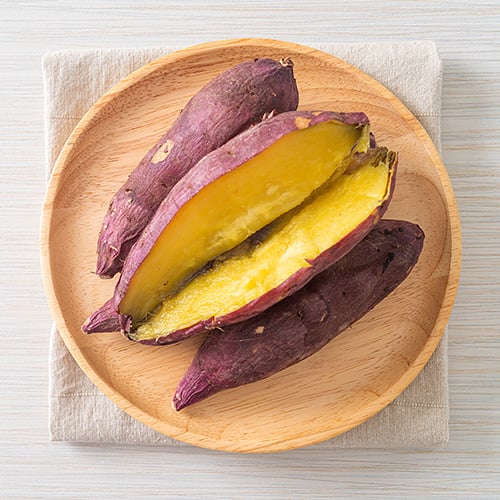

Japanese sweet potatoes, also known as Satsuma-imo, are a popular variety of sweet potatoes that originated in Japan. This variety of sweet potato has dark red or purple skin with pale flesh that turns buttery yellow as it cooks. It has a sweet, nutty flavor similar to a roasted chestnut and a dense texture that's compared to thick pudding. Considered starchier than other sweet potatoes, the Japanese sweet potato crisps up when roasted or fried but remains soft in the middle. Japanese sweet potatoes are widely used in both sweet and savory dishes. Their natural sweetness makes them a great choice for desserts such as pies, cakes, and puddings. They can also be roasted, mashed, or fried to create savory dishes like fries, hash browns, or casseroles. A popular variety in Japan, this sweet potato is a favorite street snack sold by vendors during the fall and winter.
- Japanese Sweet Potato Texture: Starchy
- Japanese Sweet Potato Skin Color: Dark red or purple skin
- Japanese Sweet Potato Flesh Color: Pale flesh that turns yellow when cooked
- Best Uses for Japanese Sweet Potatoes: Baking, mashing, roasting, deep frying
- Other Names for Japanese Sweet Potatoes: Satsuma-imo, Japanese White Yam
13. Hannah Sweet Potato

Hannah sweet potatoes are characterized by their light tan skin and pale flesh, making them stand out from other varieties. Their natural sweetness and slightly nutty taste pair well with both traditional and exotic spices, making them a popular choice for chefs looking to add depth and complexity to their dishes. Hannah sweet potatoes have a firm, dense texture similar to a white potato and will hold their shape better than other sweet potato varieties. They can be diced or cubed and used in soups, stews, or stir-fries. Because they are so firm, they require longer cook times than softer, orange sweet potato varieties. These sweet potatoes are a great option for both savory and sweet dishes, as they can be roasted, mashed, baked, or fried to create a variety of flavorful meals. For a unique presentation, try the Hasselback cooking method with Hannah sweet potatoes.
- Hannah Sweet Potato Texture: All-purpose
- Hannah Sweet Potato Skin Color: Tan skin
- Hannah Sweet Potato Flesh Color: Yellow or cream-colored flesh
- Best Uses for Hannah Sweet Potatoes: Pureeing, mashing, baking, deep frying, roasting, simmering
- Other Names for Hannah Sweet Potatoes: Yellow Hannah, Sweet Hannah, Hannah Yams
14. Jewel Yams

Jewel yams are characterized by their deep orange flesh and vibrant red skin, making them not only visually appealing but also a flavorful addition to a variety of dishes. Don't be confused by the name of this sweet potato. It's actually not a true yam at all. In this case, yam is just a nickname for a softer variety of sweet potato. The Jewel yam has starchy flesh that becomes very soft and moist when cooked, making them ideal for mashing, roasting, or baking. They can be used in a variety of dishes, including soups, stews, casseroles, and desserts. Avoid applications that require the tuber to keep its shape, like dicing for stir fries or soups.
- Jewel Yam Texture: Starchy
- Jewel Yam Skin Color: Copper-colored skin
- Jewel Yam Flesh Color: Deep orange flesh
- Best Uses for Jewel Yams: Baking, mashing, roasting, pureeing
- Other Names for Jewel Yams: Jewel Sweet Potato
Potato FAQ
Below, we answer some of the most frequently asked questions about potato types:
Potato Classifications
Potatoes can be categorized into seven different classifications based on their color and shape. Each of these potato classifications contains countless different varieties that have been cultivated over time. Here in the US, we classify potatoes as one of these seven descriptors:
- Russet Potatoes - Russets are large potatoes with rough brown skin and pale flesh.
- Yellow Potatoes - Yellow potatoes have thin gold skin and yellow flesh.
- White Potatoes - White potatoes have thin beige or tan skin with pale flesh.
- Red Potatoes - Red potatoes have thin red skin and pale flesh.
- Purple or Blue Potatoes - Blue potatoes have dark purple or blue skin with matching purple flesh.
- Fingerling Potatoes - Fingerling potatoes have a small, tubular shape and have a variety of skin and flesh characteristics.
- New Potatoes - New potatoes are young potatoes that have been harvested early. They have thin, delicate skin and creamy flesh. Also called baby potatoes, they come in a variety of colors.
Waxy vs Starchy Potatoes
The difference between waxy and starchy potatoes depends on the texture of the flesh of the potato. Starchy potatoes, such as Russet and Purple Peruvian varieties, have a high starch content and low moisture, making them ideal for baking, frying, and mashing. They have a fluffy texture when cooked and absorb flavors well, making them great for dishes like french fries and mashed potatoes. On the other hand, waxy potatoes, like Red Bliss and new potatoes, have a lower starch content and higher moisture, resulting in a firm texture when cooked. Waxy potatoes hold their shape well, making them perfect for salads, soups, stews, and dishes where you want the potato to remain intact.
Potato Uses Video
Check out our video to learn the difference between starchy, waxy, and all-purpose potatoes:
Types of Potatoes Chart
 Printable Version
Printable Version
When forming your recipes, make sure to choose the right potato for the job. Each variety of potato has unique qualities that make it more suited for certain cooking methods. Whether you're incorporating them into your Thanksgiving dinner for a crowd or adding a new side to your restaurant menu, there is a potato type to perfectly fit the preferences of your guests and customers.