Seafood is a staple on many menus, but can be intimidating to prepare. Due to their short muscle fibers, seafood is easily overcooked. However, in an attempt to prevent rubbery and dry dishes, seafood can end up undercooked, leading to potential risks like foodborne illnesses. By knowing and adhering to the recommended cooking temperatures, chefs can choose the best seafood for their restaurant and maintain the integrity of its flavor, texture, and overall quality while keeping their diners safe.
Shop All Seafood Pots and Serving Trays
Safe Cooking Temperature for Seafood
Safe cooking temperatures are crucial when preparing seafood to prevent foodborne illnesses. The FDA recommends cooking seafood to an internal temperature of 145 degrees Fahrenheit (63 degrees Celsius) to kill harmful bacteria. This temperature applies to all types of seafood, including fish, shrimp, scallops, and lobster. Despite the guideline, many chefs would agree that this temperature isn’t always ideal for the perfect texture and flavor profiles. In these circumstances, a consumer advisory is required on a menu to indicate that consuming raw or undercooked seafood may put customers at risk for foodborne illnesses. To reduce the risk, use a reputable fishmonger when selecting seafood for your menu, have a HACCP plan in place when accepting fish deliveries, and practice proper cold food storage before the fish is cooked.
How to Check the Temperature of Seafood
To ensure seafood is cooked safely and to the proper temperature, use a food probe thermometer. Check the temperature by inserting the thermometer into the thickest part of the seafood, avoiding the shell while cooking lobster. Wait until the number on the thermometer settles or passes the safe food temperature. Seafood internal temperatures may continue to rise once it is pulled from the heat, so it is a good practice to check once more before serving if it has not reached the desired temperature during the cooking process.
Seafood Internal Temp
While the FDA recommends 145 degrees Fahrenheit for safe seafood temperatures, achieving the ideal texture and mouthfeel may have you considering serving your dishes at lower temperatures. We’ve created a list of seafood cooking temperatures to help you prepare succulent seafood that will have your customers coming back for more. (Be sure to include a consumer advisory on your menu if you plan to cook seafood below 145 degrees Fahrenheit.)
1. Salmon Internal Temp

Salmon is a flavorful seafood option that can be prepared in a variety of ways, from baking to grilling the fish. The FDA recommends cooking salmon to an internal temperature of 145 degrees Fahrenheit. At this temperature, the salmon will be opaque and flake easily with a fork. Because of its mild flavor, salmon pairs beautifully with diverse seasonings and sauces, from a citrus and herb to a sweet teriyaki glaze.
If you prefer your salmon to be a little more rare or medium-rare for a moist and tender mouthfeel, you can cook it to an internal temperature of 110-130 degrees Fahrenheit (49-54 degrees Celsius). Keep in mind that cooking salmon at lower temperatures may not kill all bacteria, so it's important to use high-quality, fresh salmon from a reputable source. Use a meat thermometer, inserting it into the thickest part, to ensure that your salmon reaches the correct internal temperature.
- Salmon Cooking Temperature: 110-145 degrees Fahrenheit
- Ways to Cook Salmon: Grilling, baking, pan-searing, on the skin
- How to Tell If Salmon Is Done: The flesh of salmon should easily flake with a fork and appear an opaque light orange color when done.
- How Long to Cook Salmon: Times will vary depending on the size of the cut and cooking method. The baking recommendation is 12-15 minutes at 400 degrees Fahrenheit per 1-inch thickness. For pan-searing, cook the salmon skin-side down for 6-8 minutes on medium-high heat, then flip for 1-2 minutes.
2. Shrimp Internal Temp

With various types of shrimp available, this crustacean is a popular seafood choice for many commercial kitchens. Whether grilling, sauteing, poaching, or boiling shrimp, it's essential to monitor the internal temperature to ensure they are safe to consume. The FDA-recommended cooking temperature for shrimp is 145 degrees Fahrenheit (63 degrees Celsius). At this temperature, shrimp should be opaque and firm to the touch with a pearly, slightly orange color. Undercooked shrimp may appear translucent and soft, while overcooked shrimp can become tough and chewy.
To avoid serving rubbery shrimp, some chefs may choose to undercook them in order to achieve a softer and juicier texture. For tender shrimp, cook to an internal temperature of 120-130 degrees Fahrenheit. If you choose to do so, be sure to clearly indicate to your customers that your shrimp has been intentionally undercooked. Remember that shrimp will continue to cook even after it is removed from the heat source, so it's crucial to factor in this carryover cooking to prevent overcooking.
- Shrimp Cooking Temperature: 120-145 degrees Fahrenheit
- Ways to Cook Shrimp: Boiling, grilling, sauteing, deep-frying
- How to Tell If Shrimp Is Done: The shrimp should turn orange and opaque, the flesh should be firm to the touch, and the tails should curl inward.
- How Long to Cook Shrimp: Larger shrimp may require longer cooking times, while smaller shrimp cook more quickly. Boiling or grilling shrimp typically takes 2-3 minutes per side, while baking or broiling may take 6-8 minutes.
3. Tuna Internal Temp

Tuna is a versatile fish that is commonly enjoyed rare or medium-rare due to its firm texture and rich flavor. The internal temperature of tuna should reach a minimum of 145 degrees Fahrenheit (63 degrees Celsius) to be considered safe for consumption. However, because it loses moisture so rapidly, tuna steaks are often seared to 115 degrees Fahrenheit or under. For this reason, choose high-quality sushi grade fish that has been flash frozen immediately after being caught to reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses. It is still important to include a consumer warning when serving fish under the temperature of 145 degrees Fahrenheit.
Tuna can be prepared in various ways, including grilling, searing, or baking. The most popular method is to sear it quickly over high heat to create a crispy exterior while leaving the center rare or medium-rare. This method of cooking preserves the natural flavors of the fish and provides a delightful contrast in textures.
- Tuna Cooking Temperature: 110-145 degrees Fahrenheit
- Ways to Cook Tuna: Pan-searing, grilling, baking, sous vide
- How to Tell If Tuna Is Done: When seared, the exterior of the tuna will change color from pink or purple to beige or grey and be firm. The interior should retain its color and remain soft and juicy.
- How Long to Cook Tuna: For seared tuna steaks, cook them for about 1-2 minutes per side over high heat. Grilled tuna may take 2-3 minutes per side for medium-rare and an extra 2-3 minutes for medium-well.
4. Cod Internal Temp
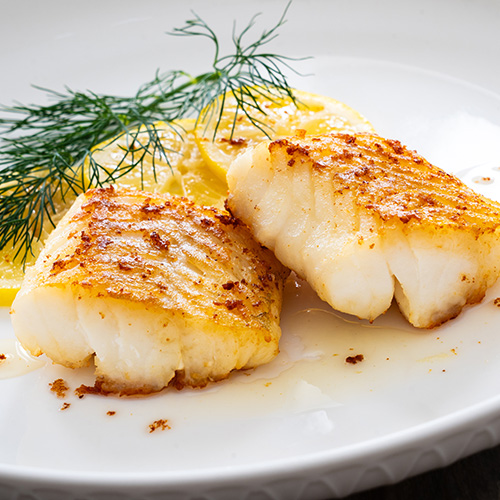

Cod is a popular seafood choice, especially in the culinary world of fish and chips. When it comes to cooking cod, achieving the perfect internal temperature is key to ensuring a delicious and safe dish. Cod is typically cooked to a medium doneness, which means the internal temperature should reach between 130-135 degrees Fahrenheit (54-57 degrees Celsius). This temperature range produces a tender and flaky texture; however, it is not high enough to eliminate the risk of foodborne illnesses. To be considered completely safe to eat, cod should be cooked to 145 degrees Fahrenheit.
Cod can be prepared in a multitude of ways, from baking and grilling to pan-searing and broiling. Overcooking cod can lead to a dry and rubbery texture. The flesh will be white and opaque when it is ready to be served. To ensure that your cod dishes are cooked to perfection, it is essential to closely monitor the internal temperature of the fish.
- Cod Cooking Temperature: 130-145 degrees Fahrenheit
- Ways to Cook Cod: Deep-frying, baking, steaming, poaching
- How to Tell If Cod Is Done: To determine if cod is done, look for the flesh to turn completely white in appearance and easily flake with a fork. The fish should be firm but still moist.
- How Long to Cook Cod: Cod typically takes around 10-15 minutes to bake thoroughly in the oven. It usually takes about 3-5 minutes to deep-fry cod for fish and chips. Pan-searing cod requires approximately 2-3 minutes per side.
5. Lobster Internal Temp
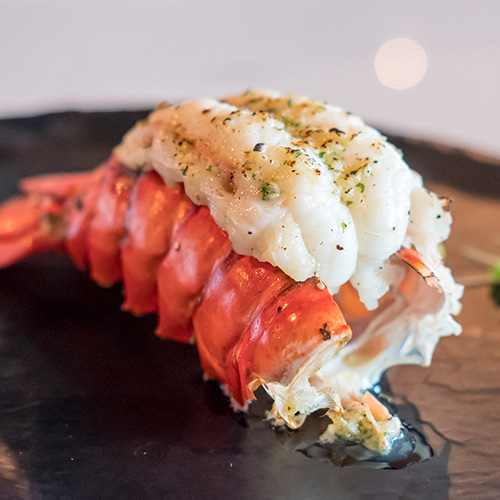

Lobster is a prized delicacy enjoyed in various culinary preparations, ranging from lobster bisque to lobster rolls. The internal temperature of lobster should reach a minimum of 145 degrees Fahrenheit (60 degrees Celsius) to kill foodborne-illness causing bacteria. However, most chefs will pull lobster from the heat at 135 degrees Fahrenheit to keep it from losing too much moisture, which would result in tough and rubbery meat, diminishing its delicate flavor and texture. Indicate on your menu if your lobster is intentionally undercooked.
Whether you’re boiling, steaming, baking, or grilling lobster, monitor the internal temperature closely to achieve the perfect balance of tenderness and flavor. To accurately measure the internal temperature of a lobster, use a reliable food thermometer inserted into the thickest part of the meat, such as the tail or claw, without touching the shell. Lobster meat should be opaque and white when fully cooked, and the shells should turn bright red.
- Lobster Cooking Temperature: 135-145 degrees Fahrenheit
- Ways to Cook Lobster: Boiling, steaming, grilling, baking
- How to Tell If Lobster Is Done: When lobster is done, the shell will turn bright red, the meat will be opaque and white, and the tail will curl under the body.
- How Long to Cook Lobster: A 1-pound lobster will take around 7-10 minutes to cook fully. Grilled lobster tails take approximately 6-10 minutes to cook on a medium to medium-high heat.
6. Scallops Internal Temp
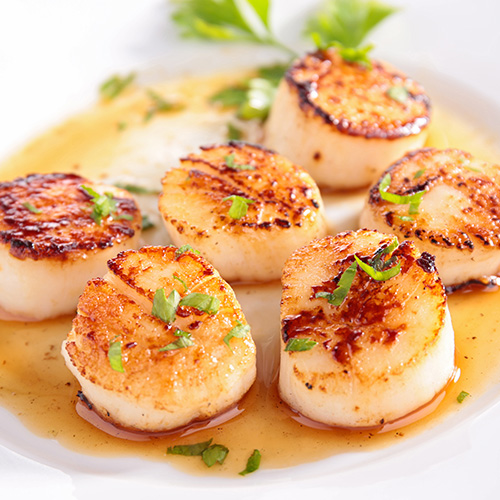

Scallops, known for their delicate flavor and tender texture, are an elegant addition to restaurant seafood menus. The texture of scallops can change rather quickly, so it is crucial to pay attention to their internal temperature to ensure they are cooked properly and safely. The ideal internal temperature for scallops to achieve that melt-in-your-mouth texture is 125-130 degrees Fahrenheit (52-54 degrees Celsius); however, this will not kill potentially harmful bacteria. Scallops should reach 145 degrees Fahrenheit to be deemed safe to consume.
At 125-130 degrees Fahrenheit, scallops are cooked to a medium-rare to medium doneness, which preserves their natural sweetness and succulence. Overcooking scallops can result in a rubbery texture and loss of flavor, so some chefs pull scallops while they are still 10 degrees below the desired temperature to allow the carryover heat to bring them up to the desired doneness. To accurately measure the internal temperature of scallops, use a food thermometer inserted into the thickest part of the scallop. They should be firm and opaque when done, with slight springiness to the touch.
- Scallops Cooking Temperature: 125-145 degrees Fahrenheit
- Ways to Cook Scallops: Pan-searing, grilling, poaching, baking
- How to Tell If Scallops Are Done: To determine if scallops are done, look for a pearly white opaque color and a firm texture. Overcooked scallops will be tough and rubbery. The flesh should have some spring to it when pressed and should cut like butter.
- How Long to Cook Scallops: For grilled and pan-seared scallops, cook for 2-3 minutes per side over medium-high heat. Poached scallops can take approximately 5-10 minutes to cook.
Seafood Cooking Temp FAQ
We address some of the most frequently asked questions when it comes to seafood temperatures:
Can You Refreeze Fish After Cooking?
Once fish has been cooked, it is generally safe to refreeze it as long as it has been handled properly throughout the cooking process. If the fish was thawed in the refrigerator, cooked to a safe internal temperature of 145 degrees Fahrenheit, and promptly refrigerated after cooking, it can be refrozen. However, it is important to note that the quality of the fish may degrade slightly upon refreezing, so it is best to consume it within a reasonable timeframe to maintain optimal taste and texture.
How Long Can Cooked Seafood Sit Out?
Cooked seafood should not sit out at room temperature for more than 2 hours. Bacteria can grow rapidly on seafood that is left out for too long, potentially leading to foodborne illnesses. To keep cooked seafood safe, it should be refrigerated within 2 hours of cooking. If the ambient temperature is above 90 degrees Fahrenheit, the window for safe storage decreases to just 1 hour.
Give your customers a high-quality experience at your establishment by learning safe seafood handling practices. By ensuring that seafood reaches the right temperature, you not only provide a delicious meal, you can also guarantee a safe meal. Elevate your dining presentation by plating those elegant dishes like a pro.
For more products related to seafood, check out our seafood display cases, seafood tools, and canned seafood.