From traditional whole milk to plant-based alternatives, each type of milk offers unique flavor profiles, uses, and benefits. Understanding the different milk types available can help you cater to various dietary preferences and requirements, ensuring that you can meet the diverse needs of your customers whether you're filling a milk cooler in a cafeteria or are looking for milk alternatives for your cafe. We created a list of the most common types of milk you can stock up on for your foodservice establishment.
Shop All MilkTypes of Milk
When it comes to selecting the right type of milk for your commercial kitchen, there are several options to consider. Your menu and your customers’ dietary restrictions can shape the types of milk you carry in your establishment. From offering hot coffees to preparing frozen desserts, these are just some of the milk options to choose from:
1. Whole Milk

Whole milk is defined as cow’s milk that contains no less than 3.25% milk fat by weight. This higher fat content gives whole milk its characteristic smooth mouthfeel and full-bodied flavor. It is often used in cooking and baking to add moisture, richness, and depth of flavor to dishes. In addition to its culinary uses, whole milk is also a popular choice for beverages such as coffee, tea, and smoothies. Its creamy consistency enhances the taste and texture of these drinks, making them more indulgent and satisfying. Whole milk is a good source of essential nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and protein. These nutrients are considered important for maintaining strong bones, supporting overall health, and providing energy.
- What Does Whole Milk Taste Like? Full-bodied, smooth, and rich
- Whole Milk Uses: In rich desserts like pudding and custards, for coffee drinks like lattes and cappuccinos, to make frozen treats like milkshakes and ice cream
- Is Whole Milk Lactose-Free? No
- Is Whole Milk Dairy-Free? No
2. 2% Milk

2% milk, also known as reduced-fat milk, is a type of cow's milk that contains 2% milk fat by weight, making it a lighter option compared to whole milk, which typically contains around 3.25% milk fat. Due to its moderate milk fat content, 2% milk strikes a balance between flavor and health benefits, making it a popular choice for those looking to reduce their fat intake without sacrificing taste and nutritional content. It is a versatile option for both cooking and enjoying on its own as a refreshing cold glass of milk or in cereal. From creating sauces and soups to producing baked goods with a slightly richer flavor than skim milk, 2% milk is a preferred option in culinary kitchens. It can be used to create lattes, cappuccinos, and other espresso-based drinks, providing a creamy texture and pleasant taste without the heaviness of whole milk.
- What Does 2% Milk Taste Like? Velvety and slightly sweet with a subtle richness
- 2% Milk Uses: On its own or in cereal, added to coffee or tea, used to make sauces and soups, for baking cakes and bread
- Is 2% Milk Lactose-Free? No
- Is 2% Milk Dairy-Free? No
Whole Milk vs 2 Percent
Whole milk and 2% milk are two popular varieties that are widely used in commercial food service establishments. Whole milk, as the name suggests, contains a higher fat content compared to 2% milk. It typically contains at least 3.25% milk fat, giving it a rich and creamy texture. 2% milk, also known as reduced-fat milk, has had some of the milk fat removed, resulting in a lower fat content of around 2%. This makes 2% milk a lighter option while still providing a decent amount of creaminess.
3. Low Fat Milk

Low-fat milk is cow’s milk that typically contains around 1% milk fat, compared to the 3.25% found in whole milk. It is a lower-fat alternative to whole milk while still retaining essential nutrients such as protein, calcium, and vitamins like vitamin D. Low-fat milk is a popular choice for foodservice establishments looking to offer healthier options to their customers. It is often used in baking recipes to add moisture and richness to baked goods without the added fat content of whole milk or cream. Low-fat milk can be used in cakes, muffins, bread, and other baked items to achieve a lighter texture and tender crumb. It is an excellent base for smoothies in commercial settings such as smoothie bars and cafes.
- What Does Low Fat Milk Taste Like? Mild flavor, subtle sweetness, and light mouthfeel
- Low Fat Milk Uses: As a substitute for whole milk in baking recipes like muffins and cookies, to add light creaminess to smoothies and coffee drinks, in breakfast foods like cereal and oatmeal
- Is Low Fat Milk Lactose-Free? No
- Is Low Fat Milk Dairy-Free? No
4. Skim Milk

Skim milk, also known as fat-free or nonfat milk, is a popular dairy product that has undergone a process to remove the majority of its fat content resulting in a product that contains less than 0.5% milk fat. This makes it a great option for smoothie and juice bars, where health-conscious clientele may be looking for low- to no-fat options. You’ll find skim milk commonly enjoyed on its own or used in a variety of culinary applications, including baking, cooking, and beverage preparation. Although you can use skim milk in any recipe that calls for milk, it is important to note that the reduction in fat may result in a slightly less creamy texture compared to whole milk. While the substitution may not be notable in a baked good, the difference in consistency may be more evident in cream-based pasta sauces or ice cream that rely on that richness.
- What Does Skim Milk Taste Like? Light sweetness and slightly watery consistency
- Skim Milk Uses: To make bread and dough for a softer and more tender final product, in beverages such as flavored milk, protein shakes, and smoothies, in the production of low-fat dairy products such as yogurt, cheese, and ice cream
- Is Skim Milk Lactose-Free? No
- Is Skim Milk Dairy-Free? No
Skim Milk vs Whole Milk
The difference between whole milk and skim milk is in the amount of milk fat they contain. Skim milk, also known as fat-free milk, contains less than 0.5% milk fat, making it a popular choice for those looking to reduce their calorie and fat intake. On the other hand, whole milk contains around 3.25% milk fat, providing a richer and creamier texture.
5. Organic Milk

Produced without the use of synthetic pesticides, hormones, or antibiotics, organic milk is considered to be a healthier and more sustainable alternative to conventional milk. Organic milk is only labeled as such after the production facility is certified organic by federal regulatory authorities. One key aspect of organic milk production is the emphasis on animal welfare. Organic dairy cows are required to have access to pasture for grazing and must be raised in a way that promotes their overall well-being. This results in a higher quality of life for the cows and can also lead to a higher quality of milk. Organic milk may contain higher levels of certain nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. With organic milk being a popular choice for many consumers seeking a more natural and environmentally friendly option, it can be a selling point on your menu.
- What Does Organic Milk Taste Like? Varies on the percentage of milk fats, typically creamy and slightly sweet
- Organic Milk Uses: In producing high-quality ice cream and frozen desserts, to complement the flavors of specialty coffee drinks, like lattes and cappuccinos, to make baked goods with an organic label
- Is Organic Milk Lactose-Free? No
- Is Organic Milk Dairy-Free? No
Back to Top
6. Raw Milk

Raw milk is milk that has not undergone any pasteurization or homogenization processes. It is collected directly from the cow, sheep, or goat and is not heated to kill bacteria. While raw milk enthusiasts claim that it has numerous health benefits, it is important to note that raw milk can also present serious health risks. One of the primary concerns associated with raw milk is the potential for contamination with harmful bacteria such as E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria. These pathogens can cause foodborne illnesses, leading to uncomfortable and highly contagious symptoms. Regulations regarding the sale of raw milk vary by state in the United States, with some states allowing its sale for human consumption while others prohibit it. Businesses in the foodservice industry should be aware of the regulations in their area and follow proper food safety practices when handling raw milk to minimize the risk of foodborne illness.
- What Does Raw Milk Taste Like? Can vary depending on factors such as the cow's diet and breed, rich with grassy or earthy notes
- Raw Milk Uses: Check with local jurisdiction if the use of raw milk is permitted in your state, sometimes used for artisan cheeses and types of yogurt
- Is Raw Milk Lactose-Free? No
- Is Raw Milk Dairy-Free? No
7. Buttermilk

Buttermilk is a versatile dairy product that has been used for centuries. Contrary to its name, buttermilk is not actually made from butter. There are two main types of buttermilk: traditional buttermilk and cultured buttermilk. Traditional buttermilk is the liquid that remains after butter is churned from cream. This type of buttermilk has a slightly tangy flavor and a thin consistency. It was commonly used in baking to add moisture to recipes but is less common in modern recipes. Cultured buttermilk is made by adding healthy bacteria cultures to milk, which ferments the milk and gives it a tangy flavor and thicker consistency. Cultured buttermilk is more commonly found in supermarkets and is often used in cooking and baking to add a subtle tanginess to recipes, like pancakes, biscuits, and cakes. It can also be used to tenderize meat and add richness to sauces.
- What Does Buttermilk Milk Taste Like? Tangy and slightly sour
- Buttermilk Milk Uses: To add tanginess and fluffy texture to biscuits, pancakes, and cakes, as a tenderizing agent in marinades for meats, as a base for salad dressings and dips
- Is Buttermilk Milk Lactose-Free? No
- Is Buttermilk Milk Dairy-Free? No
8. Condensed Milk
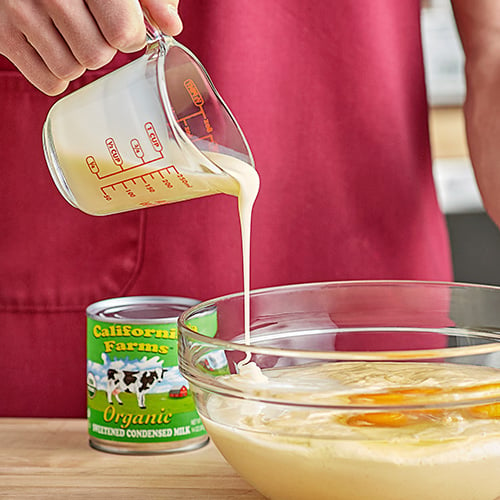

Condensed milk is made by evaporating most of the water content from cow's milk and adding sugar, resulting in a thick, sweet, and creamy product. Due to its low water content and high sugar content, condensed milk can be stored for an extended period without refrigeration, making it a convenient option for commercial kitchens and food manufacturers. In baking applications, condensed milk is often used to add richness and moisture to recipes. It can be found in a variety of desserts such as fudge, pies, and cakes, where its sweet flavor enhances the overall taste of the final product. Condensed milk can also be used to make caramel and Hispanic dishes like dulce de leche and flan, adding an indulgent element to sweet treats. Use condensed milk to sweeten strong coffee or tea, or to make international options like Vietnamese iced coffee and Thai iced tea.
- What Does Condensed Milk Taste Like? Sweet and caramel-like with a thick consistency
- Whole Condensed Uses: Thickening agent for sauces, custards, and ice creams, to make caramel and dulce de leche, to sweeten coffee and tea beverages
- Is Condensed Milk Lactose-Free? No
- Is Condensed Milk Dairy-Free? No
9. Lactose Free Milk

Lactose-free milk is a popular alternative for individuals who are lactose intolerant or have difficulty digesting lactose, a sugar found in milk. This type of milk is produced by adding the enzyme lactase to regular cow’s milk, which breaks down the lactose into simpler sugars, glucose, and galactose. As a result, lactose-free milk is easier for those with lactose intolerance to digest without experiencing uncomfortable symptoms. It is important to note that lactose-free milk still contains dairy and is not suitable for those following vegan diets. Lactose-free milk is available in various fat percentages, from whole milk to skim milk, and can be used as a direct substitute in cooking or beverage recipes.
- What Does Lactose-Free Milk Taste Like? Slightly sweeter than traditional cow's milk, varies on the amount of milk fat
- Lactose-Free Milk Uses: To prepare recipes, including baked goods, sauces, soups, and beverages, for those with lactose intolerance
- Is Lactose-Free Milk Lactose-Free? Yes
- Is Lactose-Free Milk Dairy-Free? No
10. Oat Milk
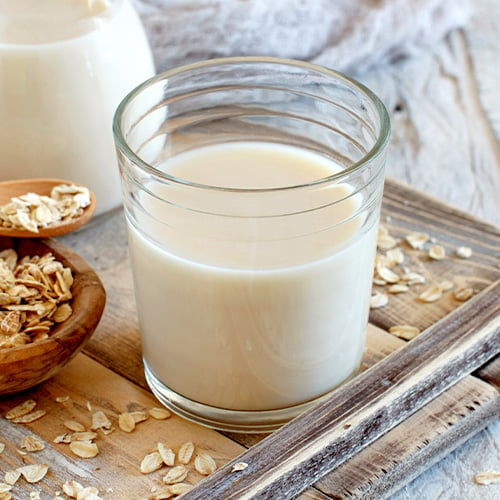

Oat milk is a popular dairy alternative that has gained significant traction in the commercial food industry in recent years. Made from a mixture of soaked oats and water, oat milk offers a creamy texture and a slightly sweet flavor. This plant-based milk is suitable for those with lactose intolerance, nut allergies, or dietary preferences that exclude dairy products. Oat milk is often fortified with vitamins and minerals, such as calcium and vitamin D, to mimic the nutritional content of cow's milk. It can be frothed for use in specialty coffee beverages, added to protein smoothies, or used as a base for dairy-free sauces and desserts. Its neutral flavor profile also makes it an excellent substitute for cow's milk in baking and cooking.
- What Does Oat Milk Taste Like? Subtle sweet and oaty taste with hints of nuttiness and a smooth finish
- Oat Milk Uses: Frothed for foam and latte art, in espresso-based beverages, in baked goods, cooked recipes, and sauces for those with food allergies or intolerances
- Is Oat Milk Lactose-Free? Yes
- Is Oat Milk Dairy-Free? Yes
Oat Milk vs Whole Milk
Oat milk is a plant-based alternative to traditional dairy milk, while whole milk is a dairy product that contains all the fat and nutrients naturally present in milk. Oat milk is naturally lactose-free, made by soaking and blending oats with water, then straining the mixture to remove solids. It is often used as a substitute for whole milk to mimic the creamy texture.
Back to Top
11. Almond Milk
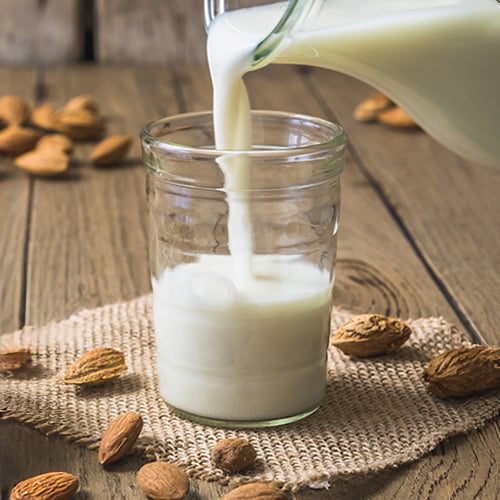

Almond milk is a plant-based beverage made from ground almonds and water. It is naturally lactose-free, making it suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Almond milk is rich in vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin E, calcium, and magnesium, making it a nutritious choice for those looking to boost their intake of essential nutrients. With its uniquely nutty flavor, it can be used as a substitute for dairy milk in smoothies, baked goods, and sauces that benefit from that flavor profile. Be sure to list when almond milk is used in a recipe to protect those with tree nut allergies.
- What Does Almond Milk Taste Like? Nutty flavor with a thin consistency
- Almond Milk Uses: Used in beverages like lattes, cappuccinos, and smoothies, as a substitute in baking and cooking to create dairy-free dishes
- Is Almond Milk Lactose-Free? Yes
- Is Almond Milk Dairy-Free? Yes
Almond Milk vs Whole Milk
Almond milk is a plant-based alternative to whole milk that is made from almonds and water. It is naturally lactose-free and suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Whole milk is a dairy product that contains a higher fat content compared to almond milk. While whole milk is rich and creamy, almond milk has a thin consistency which may require recipe modifications when using it as a substitution. Almond milk is lower in calories and fat compared to whole milk, making it a popular choice for health-conscious consumers.
Oat Milk vs Almond Milk
Oat milk and almond milk are popular dairy alternatives with distinct characteristics. Oat Milk is safe for those with nut allergies, while almond milk is not. Oat milk, made from oats, has a lush texture and a slightly sweet flavor, making it a great addition to coffee and baked goods. It is also a good source of fiber and can be frothed for lattes. Almond milk, on the other hand, is made from almonds and has a nutty taste. It is lower in calories and sugar than oat milk, making it a suitable option for those watching their intake. Almond milk is also a good source of vitamin E and can be used in both sweet and savory dishes.
12. Coconut Milk
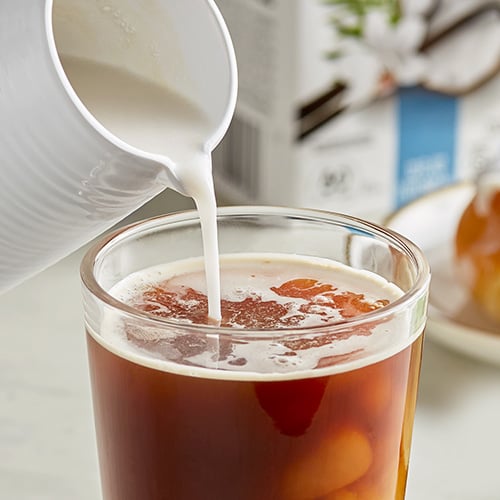

Coconut milk is a popular dairy alternative that is derived from the white flesh of mature coconuts. It is known for its rich and creamy texture, as well as its distinct tropical flavor. There are two main types of coconut milk: thick coconut milk and thin coconut milk. Thick coconut milk is made by grating the flesh of the coconut and extracting the rich, lush liquid. Closer in consistency to coconut cream, this type of coconut milk has a higher fat content and is often used in rich dishes such as curries and desserts. Thin coconut milk, on the other hand, is made by diluting the thick coconut milk with water. It has a lighter consistency and is commonly used in soups, smoothies, and sauces. Because of its distinct flavor, it may not be the most appropriate substitution for traditional cow’s milk.
- What Does Coconut Milk Taste Like? Rich and creamy with a hint of tropical coconut essence
- Coconut Milk Uses: To add a velvety texture to curries, soups, and sauces, in coconut milk-based drinks, cocktails, and smoothies, in dairy-free ice cream and frozen desserts
- Is Coconut Milk Lactose-Free? Yes
- Is Coconut Milk Dairy-Free? Yes
13. Soy Milk
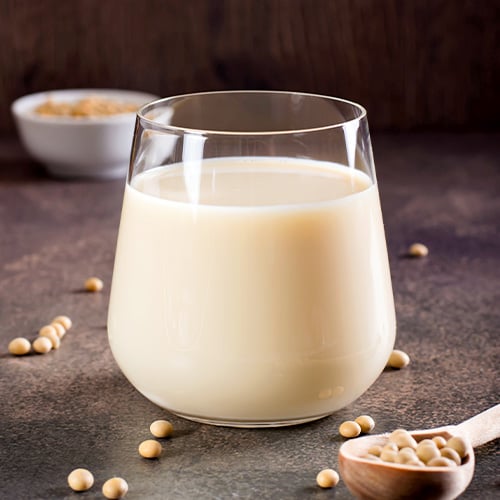

Soy milk is derived from soybeans and is a rich source of protein, making it a preferred choice for individuals following a vegetarian or vegan diet. Soy milk is naturally lactose-free but unsuitable for those with soy allergies, meaning that products made with soy milk must be appropriately labeled. Baristas will often use soy milk in coffee shops and cafes as a dairy-free alternative for lattes, cappuccinos, and other specialty coffee drinks. The neutral flavor makes it a good option in sweet and savory dishes, including soups, sauces, and baked goods. Soy milk can also be flavored with vanilla, chocolate, or other additives to enhance its taste and appeal to a wider audience.
- What Does Soy Milk Taste Like? Mild sweetness with slightly grassy or bean-like undertones
- Soy Milk Uses: Enjoyed on its own or flavored, in cereal and oatmeal, to add creaminess to vegan and vegetarian dishes like plant-based mac and cheese and dairy-free risottos
- Is Soy Milk Lactose-Free? Yes
- Is Soy Milk Dairy-Free? Yes
14. Hemp Milk

Hemp milk is a plant-based alternative to traditional dairy milk made from the seeds of the hemp plant. Hemp milk is rich in essential fatty acids, including omega-3 and omega-6, and is naturally free of cholesterol and lactose. One of the key advantages of hemp milk is its environmental sustainability. Hemp plants require less water and land compared to traditional dairy farming, making hemp milk a more environmentally friendly choice for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint. In terms of flavor, hemp milk has a slightly nutty taste that pairs well with cereals, smoothies, and coffee. It also has a texture similar to dairy milk, making it a versatile alternative in culinary applications.
- What Does Hemp Milk Taste Like? Slightly nutty and earthy taste with a hint of sweetness
- Hemp Milk Uses: Served on its own as a refreshing drink, used as a base for smoothies, shakes, added to coffee, tea, and hot chocolate, to create dairy-free puddings, custards, and ice creams
- Is Hemp Milk Lactose-Free? Yes
- Is Hemp Milk Dairy-Free? Yes
15. Cashew Milk

Cashew milk is a plant-based milk alternative that has gained popularity due to its creamy texture and mild, slightly sweet flavor. Made from a blend of cashews and water, cashew milk is a great choice for those with dietary restrictions, as it is naturally free of lactose, dairy, and soy. In commercial settings, cashew milk can be used as a dairy alternative in baked goods, beverages, sauces, and dressings. Its smooth texture and subtle flavor make it a popular choice for adding richness to dishes without overpowering other ingredients. Due to its consistency, cashew milk can be frothed and steamed, making it a suitable option for creating lattes and cappuccinos in coffee shops and cafes. It can also be used in smoothies, milkshakes, and desserts.
- What Does Cashew Milk Taste Like? Slightly sweet flavor with a subtle nuttiness and smooth consistency
- Cashew Milk Uses: As a base for making dairy-free ice creams, puddings, and sauce, in beverages such as coffee, lattes, smoothies, and milkshakes, to create moist and tender cakes, muffins, and breads
- Is Cashew Milk Lactose-Free? Yes
- Is Cashew Milk Dairy-Free? Yes
Cashew Milk vs Almond Milk
Cashew milk and almond milk are two popular non-dairy milk options that are commonly used in commercial foodservice establishments. Cashew milk is known for its smooth texture and mild, slightly sweet flavor, making it a versatile option for various applications such as coffee beverages, milkshakes, and baked goods. Almond milk has a nuttier taste and thinner consistency. It is often preferred for smoothies and in cereal. Both cashew milk and almond milk are dairy-free, vegan-friendly options that cater to customers with restrictions or preferences.
Back to Top
Understanding the different types of milk available in the commercial food industry is essential for businesses looking to cater to diverse customer preferences and dietary needs. From whole milk for rich applications to lactose-free milk for those with dietary restrictions, each type offers unique benefits and uses. Whether used in beverages, baked goods, or savory dishes, choosing the right type of milk can elevate the quality and appeal of your menu offerings.